編譯 | 未玖
Science, 18 FEBRUARY 2022, VOL 375, ISSUE 6582
《科學》2022年2月18日,第375卷,6582期
物理學Physics
Isospin magnetism and spin-polarized superconductivity in Bernal bilayer graphene
Bernal雙層石墨烯的同位旋磁性和自旋極化超導性
▲ 作者:HAOXIN ZHOU, LUDWIG HOLLEIS, YU SAITO, LIAM COHEN, WILLIAM HUYNH, CAITLIN L. PATTERSON, ET AL.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abm8386
▲ 摘要
在傳統超導體中,庫珀配對發生在自旋相反的電子之間。
研究組觀察了當摻雜到由大垂直電場產生的鞍點範霍夫奇點時,Bernal雙層石墨烯的自旋極化超導性。他們觀察到電子相位之間的靜電柵極調諧躍遷級聯,以同位旋空間中的極化為特徵,同位旋空間由自旋和動量空間谷自由度組合定義。
雖然所有這些相在零磁場下都是金屬的,但研究組觀察到在有限磁場B‖≈150 mT平行施加於二維薄片上時,會發生向超導狀態的轉變。
超導性發生在對稱破缺轉變附近,僅存在於順磁超導體預期的B‖極限之上,觀測到的轉變臨界溫度TC≈30 mK,與自旋三重態序引數一致。
▲ Abstract
In conventional superconductors, Cooper pairing occurs between electrons of opposite spin. We observe spin-polarized superconductivity in Bernal bilayer graphene when doped to a saddle-point van Hove singularity generated by a large applied perpendicular electric field. We observe a cascade of electrostatic gate-tuned transitions between electronic phases distinguished by their polarization within the isospin space defined by the combination of the spin and momentum-space valley degrees of freedom. Although all of these phases are metallic at zero magnetic field, we observe a transition to a superconducting state at finite magnetic field B‖≈ 150 milliteslas applied parallel to the two-dimensional sheet. Superconductivity occurs near a symmetry-breaking transition and exists exclusively above the B‖ limit expected of a paramagnetic superconductor with the observed transition critical temperature TC ≈ 30 millikelvins, consistent with a spin-triplet order parameter.
材料科學Materials Science
Self-assembled monolayers direct a LiF-rich interphase toward long-life lithium metal batteries
自組裝單分子層形成富LiF介面相,實現長壽命鋰金屬電池
▲ 作者:YUJING LIU, XINYONG TAO, YAO WANG, CHI JIANG, CONG MA, OUWEI SHENG, ET AL.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abn1818
▲ 摘要
高能量密度鋰(Li)金屬電池(LMB)有望應用於儲能,但由於其電解質不可控降解,會形成不穩定的固電解質介面(SEI)。
在這項研究中,研究組設計了具有高密度和長程有序極性羧基的自組裝單分子膜(SAM),與氧化鋁塗層隔膜相連以提供強大偶極矩,從而提供多餘的電子以加速鋰雙(三氟甲磺醯)亞胺中碳-氟鍵斷裂的降解動力學。
由此可生成富氟化鋰(LiF)奈米晶的SEI,促進Li+的快速轉移,並抑制Li枝晶的生長。尤其是在高陰極負載、有限鋰過剩和低電解質條件下,SAM賦予了全電池顯著增強的迴圈能力。
因此,該工作將長期建立的SAM技術擴充套件到一個平臺,以控制電解質降解和SEI的形成,從而實現超長壽命的LMB。
▲ Abstract
High–energy density lithium (Li) metal batteries (LMBs) are promising for energy storage applications but suffer from uncontrollable electrolyte degradation and the consequently formed unstable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI). In this study, we designed self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) with high-density and long-range–ordered polar carboxyl groups linked to an aluminum oxide–coated separator to provide strong dipole moments, thus offering excess electrons to accelerate the degradation dynamics of carbon-fluorine bond cleavage in Li bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide. Hence, an SEI with enriched lithium fluoride (LiF) nanocrystals is generated, facilitating rapid Li+ transfer and suppressing dendritic Li growth. In particular, the SAMs endow the full cells with substantially enhanced cyclability under high cathode loading, limited Li excess, and lean electrolyte conditions. As such, our work extends the long-established SAMs technology into a platform to control electrolyte degradation and SEI formation toward LMBs with ultralong life spans.
地球科學Earth Science
Reducing adverse impacts of Amazon hydropower expansion
減少亞馬遜流域水電站擴建的不利影響
▲ 作者:ALEXANDER S. FLECKER, QINRU SHI, RAFAEL M. ALMEIDA, HÉCTOR ANGARITA, JONATHAN M. GOMES-SELMAN, ROOSEVELT GARCÍA-VILLACORTA, et al.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abj4017
▲ 摘要
在整個亞馬遜地區350多個地點修建水電站大壩,需要戰略評估對地球上最大、生物多樣性最豐富流域提供的眾多生態系統服務之間的權衡。這些服務在空間上是可變的,因此新建大壩的集體影響在很大程度上取決於它們的配置。
研究組使用多目標最佳化來確定選址組合,在實現能源生產目標的同時,將對河流流量、河流連通性、沉積物運輸、魚類多樣性和溫室氣體排放的影響降至最低。他們發現,不協調的、一個接一個大壩的水電擴建導致了生態系統服務效益的喪失。
將水電開發造成的進一步損害降至最低,需要考慮整個流域的各種環境影響,以及亞馬遜流域國家之間的合作。該研究結果為評估跨界流域的水電擴張提供了一個可推廣的模型。
▲ Abstract
Proposed hydropower dams at more than 350 sites throughout the Amazon require strategic evaluation of trade-offs between the numerous ecosystem services provided by Earth’s largest and most biodiverse river basin. These services are spatially variable, hence collective impacts of newly built dams depend strongly on their configuration. We use multiobjective optimization to identify portfolios of sites that simultaneously minimize impacts on river flow, river connectivity, sediment transport, fish diversity, and greenhouse gas emissions while achieving energy production goals. We find that uncoordinated, dam-by-dam hydropower expansion has resulted in forgone ecosystem service benefits. Minimizing further damage from hydropower development requires considering diverse environmental impacts across the entire basin, as well as cooperation among Amazonian nations. Our findings offer a transferable model for the evaluation of hydropower expansion in transboundary basins.
考古學Archaeology
Forgotten books: The application of unseen species models to the survival of culture
被遺忘的書籍:看不見的物種模型在文化生存中的應用
▲ 作者:MIKE KESTEMONT, FOLGERT KARSDORP, ELISABETH DE BRUIJN, MATTHEW DRISCOLL, KATARZYNA A. KAPITAN, PÁDRAIG Ó MACHÁIN, et al.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abl7655
▲ 摘要
對古代文化的研究往往因人工製品殘存而受阻,因此人們通常低估了歷史社會中文化生產的多樣性。
為了糾正這種倖存者偏差,研究組應用生態學中看不見的物種模型來衡量中世紀歐洲敘事故事的缺失,比如亞瑟王的傳奇故事。所得到的估計與缺乏的歷史證據相一致。
除了圖書館火災等事件外,研究組還發現,在面對非物質損失時,文化群體的初始均勻性是這些組合穩定性的一個被忽視因素。
研究組將島嶼文獻中提高的均勻性與島嶼群落生態和文化多樣性的類似描述聯絡起來。這些分析呼籲在遺產科學中推廣該方法。
▲ Abstract
The study of ancient cultures is hindered by the incomplete survival of material artifacts, so we commonly underestimate the diversity of cultural production in historic societies. To correct this survivorship bias, we applied unseen species models from ecology to gauge the loss of narratives from medieval Europe, such as the romances about King Arthur. The estimates obtained are compatible with the scant historic evidence. In addition to events such as library fires, we identified the original evenness of cultural populations as an overlooked factor in these assemblages’ stability in the face of immaterial loss. We link the elevated evenness in island literatures to analogous accounts of ecological and cultural diversity in insular communities. These analyses call for a wider application of these methods across the heritage sciences.
仿生學Bionics
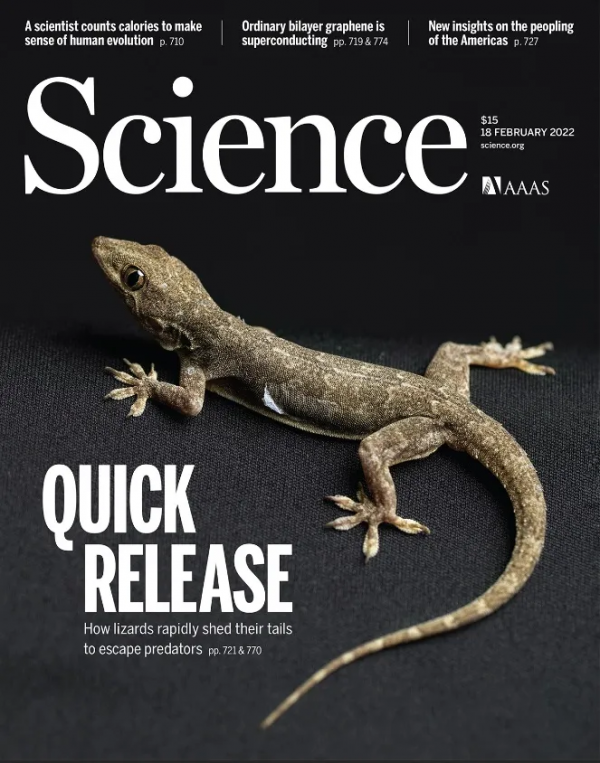
Biomimetic fracture model of lizard tail autotomy
蜥蜴自斷尾的仿生骨折模型
▲ 作者:NAVAJIT S BABAN, AJYMURAT OROZALIEV, SEBASTIAN KIRCHHOF, CHRISTOPHER J STUBBS, AND YONG-AK SONG.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abh1614
▲ 摘要
蜥蜴自斷尾是一種防禦捕食者的策略,包括在正常時間堅固附著,但在需要時迅速脫離。
研究組提出了一種利用多尺度層次結構的蜥蜴自斷尾仿生骨折模型。這些結構由均勻分佈、頂部有大量奈米孔的微柱組成,重現了在蜥蜴尾巴肌肉斷裂面上發現的高密度蘑菇狀微觀結構。
仿生實驗表明,在拉伸和剝離模式下,當奈米多孔介面與柔性微柱結合時可增強粘附力。斷裂模型表明,基於微觀和奈米結構的增韌機制是關鍵因素。
在溼潤條件下,毛細作用輔助的能量耗散與充滿液體的微間隙和奈米孔有關,進一步提高了粘附效能。這項研究為蜥蜴自斷尾提供了新見解,併為解決粘附問題提供了新的仿生思路。
▲ Abstract
Lizard tail autotomy is an antipredator strategy consisting of sturdy attachment at regular times but quick detachment during need. We propose a biomimetic fracture model of lizard tail autotomy using multiscale hierarchical structures. The structures consist of uniformly distributed micropillars with nanoporous tops, which recapitulate the high-density mushroom-shaped microstructures found on the lizard tail’s muscle fracture plane. The biomimetic experiments showed adhesion enhancement when combining nanoporous interfacial surfaces with flexible micropillars in tensile and peel modes. The fracture modeling identified micro- and nanostructure-based toughening mechanisms as the critical factor. Under wet conditions, capillarity-assisted energy dissipation pertaining to liquid-filled microgaps and nanopores further increased the adhesion performance. This research presents insights on lizard tail autotomy and provides new biomimetic ideas to solve adhesion problems.
公共衛生Public Health
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein–ACE2 complex
新冠奧密克戎變體:抗體逃逸和刺突蛋白-ACE2複合物的冷凍電鏡結構
▲ 作者:DHIRAJ MANNAR, JAMES W. SAVILLE, XING ZHU, SHANTI S. SRIVASTAVA, ALISON M. BEREZUK, KATHARINE S. TUTTLE, ET AL.
▲ 連結:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abn7760
▲ 摘要
最新報道的奧密克戎變體有望取代德爾塔成為全球最流行的新冠病毒變體。
對奧密克戎變體刺突蛋白與人血管緊張素轉換酶2(ACE2)複合物進行的冷凍電子顯微鏡(Cryo EM)結構分析顯示,在ACE2受體結合域中,突變殘基精氨酸-493、絲氨酸-496和精氨酸-498形成新的鹽橋和氫鍵。
這些強相互作用似乎補償了奧密克戎的其他突變,例如會降低ACE2結合親和力的天冬醯胺取代417位賴氨酸(K417N),從而導致德爾塔和奧密克戎變體具有相似的生化ACE2結合親和力。
中和試驗表明,顯示奧密克戎刺突蛋白的假病毒表現出更強的抗體逃逸。因此,抗體逃逸增強和ACE2結合強相互作用代表了奧密克戎變體的重要分子特徵,或有助於其快速傳播。
▲ Abstract
The newly reported Omicron variant is poised to replace Delta as the most prevalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variant across the world. Cryo–electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structural analysis of the Omicron variant spike protein in complex with human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) reveals new salt bridges and hydrogen bonds formed by mutated residues arginine-493, serine-496, and arginine-498 in the receptor binding domain with ACE2. These interactions appear to compensate for other Omicron mutations such as the substitution of asparagine for lysine at position 417 (K417N) that are known to reduce ACE2 binding affinity, resulting in similar biochemical ACE2 binding affinities for the Delta and Omicron variants. Neutralization assays show that pseudoviruses that display the Omicron spike protein exhibit increased antibody evasion. The increase in antibody evasion and the retention of strong interactions at the ACE2 interface thus represent important molecular features that likely contribute to the rapid spread of the Omicron variant.